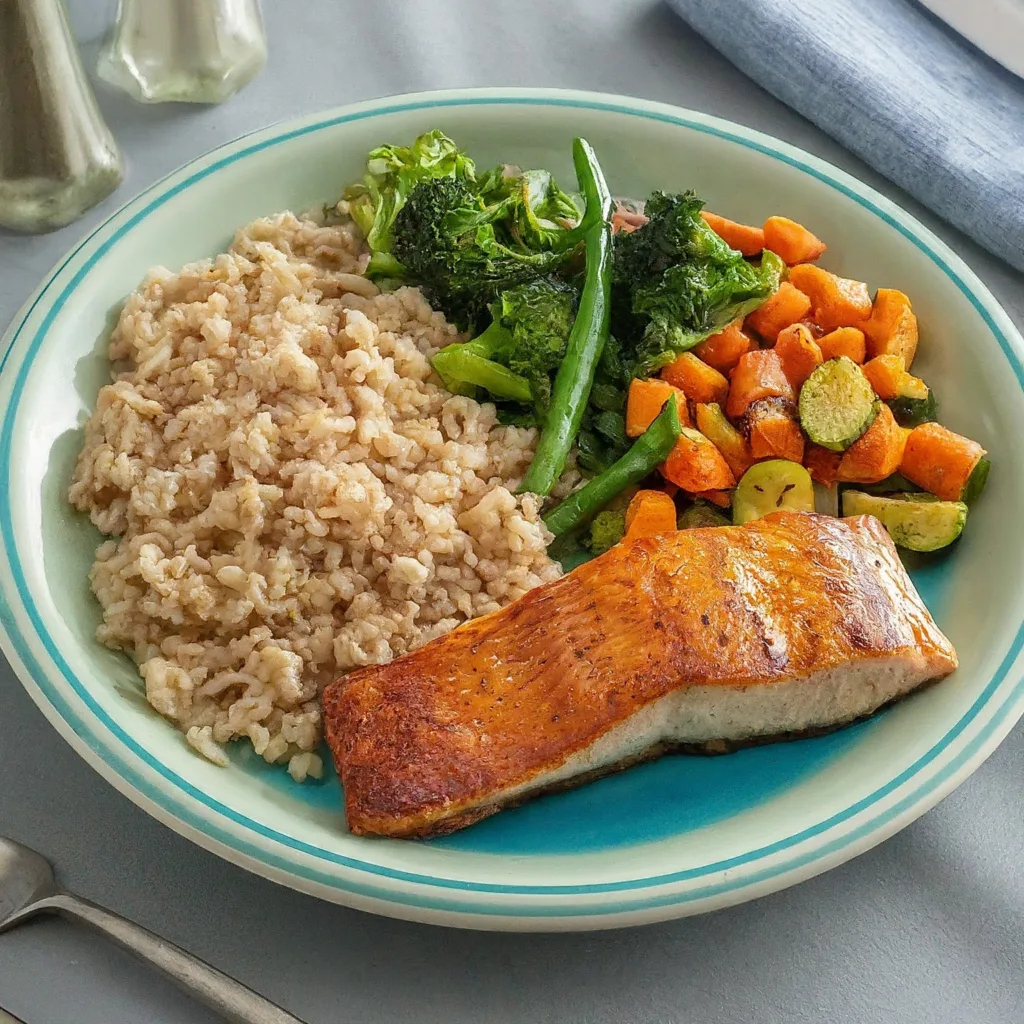The keto diet, also known as the ketogenic diet, is a high-fat, low-carbohydrate diet.
Along with its association with a century-old therapeutic seizure treatment, Dr Atkins uses the word “K” to describe his low-carb, high-fat nutritional approach, leading some to refer to the ketogenic diet as “extreme” label diet.
What is Keto diet (Ketogenic diet)?
The keto diet is known to be a low-carb diet, in which the body produces ketones in the liver to be used as energy. It is known by many names – ketogenic diet, low-carb diet, low-carb high fat (LCHF), and so on. While some of these other “names” have different standards, we’ll stick to the keto standards.
“K” = Keep carbs low;
“E” = Eat more fat;
“T” = Test ketones often;
“O” = Overdoing protein is bad.
When you eat some high carbs, your body will produce glucose and insulin. In short, eating shifts your body from burning glucose (sugar) for energy to a state of ketosis, in which your body uses ketone bodies and fats as a fuel source. Your liver makes ketone bodies from fat when your body needs it to make energy, but no glucose is present. This process usually occurs during periods of reducing carbohydrate, very limited food intake and intense exercise. 1 1 2 3
What is ketosis?
Ketosis is a daily process of the body, no matter how many carbs you consume. Your body can adapt very well, processing a variety of nutrients into the fuel it needs. Protein, fat, and carbs can all be processed for use. Eating a low-carb, high-fat diet accelerates this process, which is a normal and safe chemical reaction.
When you eat carbohydrate-based foods or high amounts of protein, your body will break it down into sugar – called glucose. Glucose is needed in the manufacture of ATP (an energy molecule), which is a fuel needed for daily activities and maintenance inside our bodies.
What if you eat enough food?
If you’ve ever used a calculator to determine your calorie needs, you’ll notice that your body uses a lot of calories. It is true that our body uses most of the nutrients we eat to sustain itself on a daily basis. If you eat enough, your body won’t need the extra glucose.
Two main things happen to glucose if your body doesn’t need it:
- Glycogenesis: Excess glucose will be converted to glycogen, and stored in the liver and muscles. Estimates suggest that only half of your daily energy can be stored as glycogen.
- Lipogenesis: If you already have enough glycogen in your muscles and liver, any excess glucose will be converted to fat and stored.
What if you don’t have much glucose or glycogen in your body?
When your body does not have access to food, such as when you are sleeping, the body burns fat and makes molecules called ketones. This is what happens on the ketogenic diet – we burn fat for energy. We can thank our body’s ability to alter metabolic pathways for that.
These ketones (acetoacetate) are created when the body breaks down fats, forms fatty acids, and is burned in the liver in a process called beta-oxidation. The end result of this process is the formation of 2 other ketones (BHB and acetone), which are used as fuel by the muscles and brain.
Although glucose is the main source of fuel for most people, these fatty acids (BHB and acetone) are used by brain cells when carbohydrate or food intake is low. In simple words, since you don’t have much glucose or glycogen, ketosis is triggered, and your body will use your stored/consumed fat as energy.
Ketosis is pretty amazing, and in fact, it’s getting even better. Studies show that the body and brain actually prefer to use ketones, which are able to run up to 70% more efficiently than glucose. From an evolutionary standpoint, this makes perfect sense.
How it works?
When fat is broken down by your liver, molecules of glycerol and fatty acids are released. Fatty acids are even broken down, in a process called ketogenesis, and ketone bodies called acetoacetate are produced.
Acetoacetate is then converted into 2 types of ketone bodies:
- Beta-hydroxybutyrate (BHB) – After being keto-adapted for some time, the muscles will convert acetoacetate to BHB as it is preferred by the brain for fuel.
- Acetone – can sometimes be metabolized to glucose, but is mostly excreted as waste. This gives off the distinctive bad breath that most ketogenic dieters are aware of.
Over time, the body will expel fewer ketone bodies, and you may find that ketosis is slowing down. It’s not, because the brain is burning BHB as fuel, and your body is trying to deliver as efficient energy to the brain as possible.
Benefits of Keto diet
- Cholesterol: Keto diet improves triglyceride levels and cholesterol levels, which are associated with the formation of arteries.
- Weight loss: Since your body is burning fat as its main source of energy, you will essentially be using your fat stores as an energy source in a fasted state. 4 5
- Diabetes and pre-diabetes: Type 2 diabetes responds well to the keto diet because of its insulin-lowering effect. Several studies show a reduction in LDL cholesterol over time and has been shown to eliminate diseases such as type 2 diabetes. 6 7
- Heart disease and metabolic syndrome: Studies have shown that heart disease and metabolic syndrome are significantly improved on the keto diet. 7
- Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s and dementia: Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s and dementia have all been shown to get better on a low-carb, moderate-protein, high-fat diet. 8
- Schizophrenia and Bipolar Disorder: Schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and other mental illnesses are treated with ketones. 9
- Narcolepsy: Narcolepsy and other sleep disorders show modest improvement in people with ketosis.
- PCOS: Women with PCOS see improvement when they start eating a low-carb, high-fat diet.
- IBS: IBS can be virtually eliminated through strategic use of the keto diet.
- GERD and heartburn: GERD and heartburn are no longer a problem when you eliminate carbohydrate-based foods that increase stomach acid. 10
- Cancer: The keto diet approach is the most effective dietary treatment for any and all types of cancer and other immunological diseases. 11
- Energy: By giving the body a better and more reliable energy source, you will feel more energized during the day. Fat has been shown to be the most effective molecule to burn as fuel.
- Acne: Recent studies have shown that there is a reduction in acne lesions and skin inflammation in 12 weeks. 12
Foods to eat and avoid keto diet
In the standard keto diet, the macronutrient requirements are as follows:
- 75% fat
- 20% protein
- 5% carbohydrates
When you translate this into a daily intake of 2,000 calories, it means you’re looking at 1,500 calories from fat, 400 calories from protein, and the remaining 100 calories from carbs.
With each gram of protein and carb yielding 4 calories, and each gram of fat yielding 9 calories, the complete breakdown above would end up with a daily grand figure of approximately:
- 166 grams of fat
- 100 grams of protein
- 25 grams of carbs
These macronutrient numbers should be at the fore of your mind when you first start on the keto diet. Just remember, always try to meet your fat requirement, limit your carb intake, and think about how much protein you’re getting into your system. If your experience is anything to go by, you’ll find that eating enough fat is a problem, at least in the early stages. This is partly because a lot of the fat you take in is present in liquid forms.
Think olive and coconut oil, or butter and lard when heated on a frying pan, all of which are high-fat essentials in the keto diet, but can easily be overlooked because they will never be a staple in a meal. You may find that keeping track of your daily fat counts helped increase your fat intake.
On days when you find the fat count a bit low, 99% dark chocolate as well as bulletproof coffee can take those numbers closer to where they’re supposed to be. Of course, there are many other high-fat foods that can do the trick too, so let’s take a look at them!
Foods to eat
There are different types of food that fall under this list. These food ideas certainly push for a higher fat content, while at the same time packing other nutrients and healthy vitamins for the body to use.
Meat and animal products
Focus on grass-fed or wild-caught seafood and pasture-raised fatty cuts of meat, avoiding processed meats and farmed meats from farmed animals as much as possible. And don’t forget about organ meats!
- Chicken
- Eggs
- Beef
- Goat
- Pork
- Lamb
- Turkey
- Organ meats
- Salmon
- Mackerel
- Tuna
- Halibut
- Cod
- Gelatin
- Venison
- Shellfish
Healthy fats
The best fats to consume on a ketogenic diet are monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, although they also contain lots of healthy saturated fats. At the risk of sounding like a broken recorder, avoid eating trans fats foods.
- Lard
- Tallow
- MCT oil
- Avocado oil
- Butter
- Chicken fat
- Coconut oil
- Duck fat
- Ghee
- Coconut milk
- Palm shortening
- Macadamia oil
- Extra virgin olive oil
- Coconut butter
Vegetables
Fresh vegetables are low in calories and rich in nutrients calories, which makes them an excellent addition to the keto diet. With the keto diet, however, there is a need to be careful about carbs, so stick to leafy greens and low-glycemic vegetables instead of root vegetables and other starchy vegetables.
- Bell peppers
- Broccoli
- Cabbage
- Cauliflower
- Artichokes
- Asparagus
- Avocado
- Cucumber
- Celery
- Kohlrabi
- Tomatoes
- Watercress
- Zucchini
- Lettuce
- Okra or ladies’ fingers
- Radishes
- Seaweed
- Spinach
Dairy products
If you are able to tolerate dairy, you can include raw dairy products, full-fat and unpasteurized in your keto diet. Keep in mind that some brands will contain a lot of sugar, which can increase the carb content, so pay attention to nutrition labels and minimize your consumption of these products. If possible, go for full-fat versions, as these will be less likely to use sugar to replace fat.
- Kefir
- Brie cheese
- Mozzarella cheese
- Swiss cheese
- Heavy cream
- Sour cream
- Cottage cheese
- Cream cheese
- Cheddar cheese
- Full-fat yogurt
Herbs and spices
Fresh herbs and dried spices are a great way to flavor your foods without adding any significant number of carbohydrates or calories.
- Cayenne
- Cardamom
- Chili powder
- Cilantro
- Cinnamon
- Cumin
- Rosemary
- Sea salt
- Sage
- Thyme
- Turmeric
- White pepper
- Basil
- Black pepper
- Ginger
- Garlic
- Nutmeg
- Oregano
- Onion
- Paprika
- Parsley
Beverages
You should avoid all sugary drinks on the keto diet, but there are some beverages you can still have in addition to good old water to add a little more variety to your fluids of choice.
- Cashew milk unsweetened
- Coconut milk
- Almond milk unsweetened
- Bone broth
- Club soda
- Coffee
- Herbal tea
- Tea
- Mineral water
- Seltzer water
Nuts And Seeds
While nuts and seeds contain carbohydrates, they are also rich in healthy fats. The below listed nuts and seeds content low to moderate in carb, so you can enjoy them as long as you watch the portion sizes. In general, an ounce or handful of nuts will be a good gauge to see how much you can eat and still stay in ketosis daily.
- Walnuts
- Nut butter
- Almonds
- Cashews
- Chia seeds
- Pumpkin seeds
- Sesame seeds
- Sunflower seeds
- Hazelnuts
- Macadamia nuts
- Pecans
- Pine nuts
- Pistachios
- Psyllium
Fruits
Fresh fruits are an excellent source of nutrition. Unfortunately, it’s also loaded with sugar, which means high in carbohydrates. There are some low- to medium-carb fruits that you can enjoy in moderation, but you have to watch what you eat!
- Blackberries
- Blueberries
- Raspberries
- Strawberries
- Cantaloupe
- Cherries
- Cranberries
- Apricot
- Grapefruit
- Honeydew
- Kiwi
- Lemon
- Lime
- Peaches
Foods to avoid
When it comes to the foods you should avoid on a keto diet, there are a few major categories to mention. First and foremost, you should avoid grains and grain-based ingredients as much as possible, as they are highest in carbohydrates. Choose healthy fats over hydrogenated oils, and try to limit your intake of starchy vegetables and high-glycemic fruits.
When it comes to sweeteners, refined sugars like white sugar and brown sugar are completely banned, and you should avoid artificial sweeteners as well. Natural sweeteners like honey, pure maple syrup and agave aren’t necessarily bad for you, but they are very high in carbohydrates. The best sweeteners to use on the keto diet are powdered erythritol, stevia and monk fruit sweetener.
Here’s a quick list of some key foods you’ll need to avoid on a keto diet:
- Rice
- Quinoa
- Corn
- Baked goods
- Baking mix
- All-purpose flour
- Wheat flour
- Pastry flour
- Cake flour
- Pasta
- Cereal
- Oats
- Muesli
- Margarine
- Corn syrup
- Snack bars
- Buckwheat
- Barley
- Couscous
- Canola oil
- Hydrogenated oils
- Milk chocolate
- Low-fat dairy
- White sugar
- Brown sugar
- Maple syrup
- Honey
- Agave
- Bananas
- Mangos
- Pineapple
- Potatoes
- Sweet potatoes
- Candy
- Ice cream
- Sport drinks
- Juice cocktail
- Soda
- Beer
A sample keto diet plan for 1 week
You can eat a variety of delicious and nutritious foods on the keto diet. It’s not all meat and fat. Vegetables are an important part of your diet. Without further ado, let’s take a look at a sample keto diet meal plan for one week:
Monday + Wednesday + Friday Meal Plan
Breakfast
| Ingredients | Quantities |
|---|---|
| Omelete yogurt: | |
| Whole eggs (large) | 2 |
| Eggs white (large) | 3 |
| Spinach | 1 cup |
| Extra-virgin olive oil | 1 tablespoon |
| Yogurt (plain) | 120 g |
| Almonds | 6 piece |
Morning snack
| Ingredients | Quantities |
|---|---|
| Protein keto shake: | |
| whey protein | 1 scoop |
| flaxseeds (ground) | 1 tablespoon |
| peanut butter | 1½ tablespoons |
| coconut milk | 130 ml |
Lunch
| Ingredients | Quantities |
|---|---|
| grilled chicken | 120 g |
| green peppers | ½ cup |
| pin nuts | 1 tablespoon |
| lettuce (shredded) | 1 cup |
| avocado | 1/4 |
Evening snack
| Ingredients | Quantities |
|---|---|
| celery (chopped) | 1 cup |
| almond butter | 16 g |
Dinner
| Ingredients | Quantities |
|---|---|
| fish | 200 g |
| egg (boiled) | 2 |
| olive oil | 1 tablespoon |
| mix green salad | 1 cup |
Before bed
| Ingredients | Quantities |
|---|---|
| cashew nuts | 30g |
Microbreakdown: Calories- 2071, Fat – 140g, Protein – 157g, Carb – 51g
Tuesday + Thursday + Saturday Meal Plan
Breakfast
| Ingredients | Quantities |
|---|---|
| Chorizo Bacon Eggs: | |
| bacon (thin and cooked) | 2 slices |
| eggs (large) | 3 |
| chorizo | 50 g |
| pepper & salt | – |
| red pepper (diced) | ½ cup |
| olive oil | 1 teaspoon |
Morning snack
| Ingredients | Quantities |
|---|---|
| Keto Coconut Shake: | |
| whey protein | 1 scoop |
| coconut (shredded) | ½ cup |
| coconut milk | 100 ml |
Lunch
| Ingredients | Quantities |
|---|---|
| Fish Zoodles Avocado Cream: | |
| zucchini (chopped) | 1 cup |
| fish | 150 g |
| avocado | 100 g |
| basil | 20 leaves |
| olive oil | 1½ teaspoon |
| mushrooms (brown) | 30 g |
| garlic cloves | 1 |
| lemon juice | ½ |
| salt | 1/4 |
Evening snack
| Ingredients | Quantities |
|---|---|
| Beef Curry: | |
| beef chuck (chopped) | 150 g |
| coconut milk (canned) | 1¼ cups |
| ginger | 1 teaspoon |
| garlic | 1 teaspoon |
| curry powder | 2 tablespoons |
| salt | – |
| cilantro (chopped) | ½ cup |
Dinner
| Ingredients | Quantities |
|---|---|
| Chicken Salad: | |
| chicken (shredded) | 100 g |
| celery (chopped) | ½ cup |
| walnuts | 5 nuts |
| avocado | ½ cup |
| cucumber (peeled) | ½ cup |
Before bed
| Ingredients | Quantities |
|---|---|
| almonds | 30g |
Microbreakdown: Calories- 2260, Fat – 153g, Protein – 150g, Carb – 64g
Sunday Meal Plan
Breakfast
| Ingredients | Quantities |
|---|---|
| Eggs Salad: | |
| whole egg (boiled) | 1 large |
| egg white | 6 large |
| green onion (chopped) | 1 cup |
| avocado (sliced) | 1 tablespoon |
Morning snack
| Ingredients | Quantities |
|---|---|
| Protein Smoothies: | |
| whey protein | 1 scoop |
| chia seeds | 2 tablespoons |
| peanut butter | 2 tablespoons |
Lunch
| Ingredients | Quantities |
|---|---|
| Paneer Bhurji Salad: | |
| paneer | 150 g |
| egg (whole) | 2 large |
| salad | 1 cup |
Evening snack
| Ingredients | Quantities |
|---|---|
| Keto Pumpkin Shake: | |
| whey protein | 1 scoop |
| pumpkin seeds | 28 g |
| cream | 2 teaspoons |
| pumpkin pie spice | 1 teaspoon |
Dinner
| Ingredients | Quantities |
|---|---|
| fish | 200 g |
| eggs (boiled) | 2 large |
| cauliflower & peas | 1 cup |
| olive oil | 1 teaspoon |
Before Bed
| Ingredients | Quantities |
|---|---|
| cashews nuts | 30 g |
Microbreakdown: Calories- 2260, Fat – 150g, Protein – 187g, Carb – 71g
- Masood W, Annamaraju P, Uppaluri KR. Ketogenic Diet. [Updated 2022 Jun 11]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK499830/[↩][↩]
- Freeman AM, Pennings N. Insulin Resistance. 2022 Sep 20. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan–. PMID: 29939616. Availale from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29939616/[↩]
- Puchalska P, Crawford PA. Multi-dimensional Roles of Ketone Bodies in Fuel Metabolism, Signaling, and Therapeutics. Cell Metab. 2017 Feb 7;25(2):262-284. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2016.12.022. PMID: 28178565; PMCID: PMC5313038.[↩]
- Bueno NB, de Melo IS, de Oliveira SL, da Rocha Ataide T. Very-low-carbohydrate ketogenic diet v. low-fat diet for long-term weight loss: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Br J Nutr. 2013 Oct;110(7):1178-87. doi: 10.1017/S0007114513000548. Epub 2013 May 7. PMID: 23651522.[↩]
- Paoli A, Bosco G, Camporesi EM, Mangar D. Ketosis, ketogenic diet and food intake control: a complex relationship. Front Psychol. 2015 Feb 2;6:27. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2015.00027. PMID: 25698989; PMCID: PMC4313585.[↩]
- Bolla AM, Caretto A, Laurenzi A, Scavini M, Piemonti L. Low-Carb and Ketogenic Diets in Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes. Nutrients. 2019 Apr 26;11(5):962. doi: 10.3390/nu11050962. PMID: 31035514; PMCID: PMC6566854.[↩]
- Rochlani Y, Pothineni NV, Kovelamudi S, Mehta JL. Metabolic syndrome: pathophysiology, management, and modulation by natural compounds. Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis. 2017 Aug;11(8):215-225. doi: 10.1177/1753944717711379. Epub 2017 Jun 22. PMID: 28639538; PMCID: PMC5933580.[↩][↩]
- Włodarek D. Role of Ketogenic Diets in Neurodegenerative Diseases (Alzheimer’s Disease and Parkinson’s Disease). Nutrients. 2019 Jan 15;11(1):169. doi: 10.3390/nu11010169. PMID: 30650523; PMCID: PMC6356942.[↩]
- Prins ML, Matsumoto JH. The collective therapeutic potential of cerebral ketone metabolism in traumatic brain injury. J Lipid Res. 2014 Dec;55(12):2450-7. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R046706. Epub 2014 Apr 10. PMID: 24721741; PMCID: PMC4242438.[↩]
- El-Serag HB, Sweet S, Winchester CC, Dent J. Update on the epidemiology of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: a systematic review. Gut. 2014 Jun;63(6):871-80. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2012-304269. Epub 2013 Jul 13. PMID: 23853213; PMCID: PMC4046948.[↩]
- Klement RJ. The emerging role of ketogenic diets in cancer treatment. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2019 Mar;22(2):129-134. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0000000000000540. PMID: 30531479.[↩]
- Melnik BC. Linking diet to acne metabolomics, inflammation, and comedogenesis: an update. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2015 Jul 15;8:371-88. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S69135. PMID: 26203267; PMCID: PMC4507494.[↩]